Stockholders’ equity: Definition, components, and calculation

This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. Equity is an important concept in finance that has different specific meanings depending on the context. Perhaps how to find stockholders equity the most common type of equity is “shareholders’ equity,” which is calculated by taking a company’s total assets and subtracting its total liabilities. Stockholders’ equity provides insight into the company’s book value, calculated as total assets minus total liabilities.
How Do You Calculate a Company’s Equity?
A summary report called a statement of retained earnings is also maintained, outlining the changes in retained earnings for a specific period. Stockholders Equity provides highly useful information when analyzing financial statements. In events of liquidation, equity holders are last in line behind debt holders to receive any payments. If a company’s equity is negative for a prolonged period of time, it can amount to balance sheet insolvency.
- It’s possible for retained earnings to represent the largest share of owner equity if growth substantially outpaces the amount of capital paid in.
- For shareholders, this component reflects the company’s ability to reinvest in itself for future growth.
- ROE is considered a measure of how effectively management uses a company’s assets to create profits.
- Modern bookkeeping services go beyond basic record-keeping, offering CFO-level insights that help businesses improve cash flow, optimize expenses, and make data-driven financial decisions.
- Treasury shares or stock (not to be confused with U.S. Treasury bills) represent stock that the company has bought back from existing shareholders.
- Nevertheless, the owners and private shareholders can still compute the firm’s equity position using the same formula and method as with a public one.
- Shareholders’ equity is the residual claims on the company’s assets belonging to the company’s owners once all liabilities have been paid down.
How to Calculate Additions to Net Working Capital

Stockholders’ equity can be calculated by subtracting the total liabilities of a business from total assets or as the sum of share capital and retained earnings minus treasury shares. It also reflects a company’s dividend policy by showing its decision to pay profits earned as dividends to shareholders or reinvest the profits back into the company. On the balance sheet, shareholders’ equity is broken up into three items – common shares, preferred shares, and retained earnings. Return on Equity is a two-part ratio in its derivation because it brings together the income statement and the balance sheet, where net income or profit is compared to the shareholders’ equity. The number represents the total return on equity capital and shows the firm’s ability to turn equity investments into profits.
What Is the Formula for Equity?
- It is the difference between shares offered for subscription and outstanding shares of a company.
- Shareholders, however, are concerned with both liabilities and equity accounts because stockholders equity can only be paid after bondholders have been paid.
- The excess value paid by the purchaser of the shares above the par value can be found in the “Additional Paid-In Capital (APIC)” line item.
- It can be defined as the total number of dollars that a company would have left if it liquidated all its assets and paid off all of its liabilities.
- Unlike common stock, preferred shares typically offer fixed dividend payments that are paid out before dividends to common shareholders.
- Some call this value “brand equity,” which measures the value of a brand relative to a generic or store-brand version of a product.
For example, if a company reports a return on equity of 12% for several years, it is a good indication that it can continue to reinvest and grow 12% into the future. Once all Accounting Security liabilities are taken care of in the hypothetical liquidation, the residual value, or “book value of equity,” represents the remaining proceeds that could be distributed among shareholders. Shareholders’ equity is adjusted to account for a number of other items found on the balance sheet, including anticipated gains not yet realized and translation on foreign currency. Lastly, if the firm’s financial leverage increases, the firm can deploy the debt capital to magnify returns.
Preferred stocks and preferred shares refer to the same thing—they are interchangeable terms. SE provides a full snapshot of a company’s financial health and performance, and it indicates the company’s financial stability. All in all, calculating the ending stockholders’ equity is a relatively simple thing to do. Doing the work longhand will give you some additional insight into what’s happening with the company and will also tell you exactly how it manages to grow or shrink its stockholders’ equity over time. The value of capital assets and property, including patents, structures, machinery, and notes receivable, are Online Accounting considered long-term assets. It’s significant to note that certain assets, such as fixed assets, do not have their recorded values increased to reflect rises in market value.

Shareholder Equity (SE): What It Is and How It Is Calculated

As per the publicly released financial data, the following information is available. In our modeling exercise, we’ll forecast the shareholders’ equity balance of a hypothetical company for fiscal years 2021 and 2022. From the viewpoint of shareholders, treasury stock is a discretionary decision made by management to indirectly compensate equity holders. Otherwise, an alternative approach to calculating shareholders’ equity is to add up the following line items, which we’ll explain in more detail soon.
- Our library of 200+ lessons will teach you exactly what you need to know to use it at work tomorrow.
- It’s like a snapshot of a company’s financial health, showing what remains for shareholders after debts are paid.
- A PIPE is a private investment firm’s, a mutual fund’s, or another qualified investors’ purchase of stock in a company at a discount to the current market value (CMV) per share to raise capital.
- As a result, many investors regard enterprises with negative shareholder equity as dangerous or unsafe investments.
- To fully understand this concept, it’s helpful to know how to calculate retained earnings, as it provides insight into a company’s profitability over time.
- Negative shareholder equity means that the company’s liabilities exceed its assets.
Examples of Stockholders’ Equity in Action
For instance, a lower shareholders’ equity can be overlooked by investors if a new company has other redeeming qualities, such as appealing annual reports or it is in an industry that shows a lot of promise. Preferred stockholders have a higher claim on the company’s total assets and earnings compared to common stockholders, but rank below bondholders in priority. In addition, there are some other less common events that can affect stockholders’ equity. If it pays $900 to redeem a $1,000 bond, then cash will fall by $900, but long-term debt will decline by $1,000, leaving stockholders’ equity to rise by the difference of $100. Unrealized losses, for example, would have to be negative because a company’s stock value cannot fall below zero.
How to calculate shareholders equity
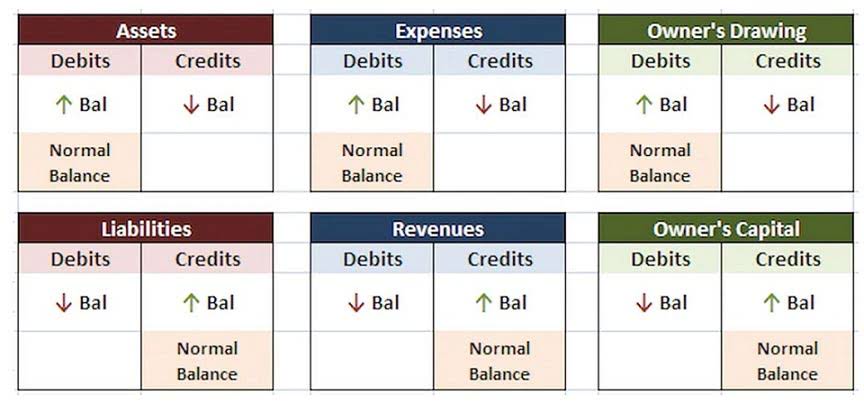
In other words, it’s what’s left for shareholders if the company sold all its assets and paid off all its debts. In this formula, the equity of the shareholders is the difference between the total assets and the total liabilities. For example, if a company has $80,000 in total assets and $40,000 in liabilities, the shareholders’ equity is $40,000. Also known as stockholders’ equity or owners’ equity, shareholders’ equity boils down to the total value of a company after it pays off all of its debts. The information required to determine shareholders’ equity is contained in a company’s balance sheet. Current assets are those that can be converted into cash in less than a year (e.g., cash, accounts receivable, inventory).
